When do we use the Present Simple and when do we use the Present Continuous?
Let’s look at each one…
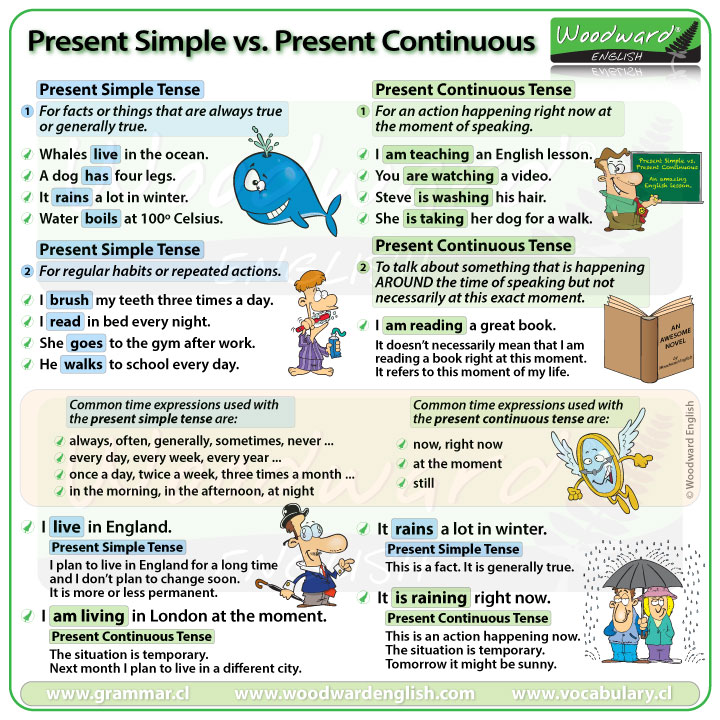
We use the present simple tense:
1. For facts or things that are always true or generally true.
The present simple tense is also used…
2. For regular habits or repeated actions
These are often daily routines and they happen always, often, generally, every week, etc.
Common time expressions used with the present simple tense are:
We use the present continuous tense:
1. An action happening right now at the moment of speaking.
When somebody is doing something right now or something is happening right now.
You can see that these actions are happening right now and they are temporary actions, normally for a short period of time.
2. To talk about something that is happening AROUND the time of speaking but not necessarily at that exact moment.
This action is in progress and hasn’t finished.
(It doesn’t necessarily mean that I am reading a book right at this moment. It refers to this moment of my life. I have started reading this book and I haven’t finished it)
(It doesn’t necessarily mean they are at the hotel right at this moment. Maybe they are at work right now or somewhere else. This situation is temporary.)
(It doesn’t necessarily mean he is learning the language right now at a desk with all of his language books. It refers to this moment of his life.)
Common time expressions used with the present continuous are:
NOTE: Sometimes the present continuous is called the present progressive in some workbooks or lessons.
Now let’s compare the two tenses together…
Here are the sentences from the beginning of this lesson.
We say I speak English, because it is a fact. I generally speak English. So we use the Present Simple tense.
We say I am speaking English because it refers to what I am doing now. It is a temporary action because in a moment I might start speaking in Spanish. So we use the Present Continuous.
Let’s compare more sentences:
We use the Present Simple for things that don’t change for a long time. I plan to live in England for a long time and I don’t plan to change soon. It is more or less permanent. But if I say:
I used the present continuous because this situation is temporary. Next month I plan to live in a different city.
We use the present simple because this is a fact or is generally true.
We use the present continuous because we are talking about an action that is happening right now. It is in progress. It will not continue forever, it is temporary. Tomorrow it might be sunny.
Compare these two sentences:
The first sentence shows the action that is happening now… he is biting his nails right now.
The second sentence uses the present simple because it is talking about his habit, sometime that he does when he is nervous. Notice how we use the present simple tense with the adverb of frequency, always.
That is what he does for a job from Monday to Friday every week. This is his routine.
It is possibly a temporary job he has this week because next week he will return to his normal job or maybe he will teach at another school next week.

Let’s compare the present simple and present continuous in affirmative sentences, negative sentences and in questions.
Here are two affirmative sentences:
Let’s look at the negative form:
We use DO NOT or DOES NOT to make negative sentences in the present simple. Remember, we can use the contractions don’t and doesn’t.
We add NOT between to be and the verb to make negative sentences in the present continuous.
And making questions:
We use DO or DOES to make questions in the present simple tense.
We change the order of the subject (pronoun) and the conjugation of the verb To Be when making questions in the present continuous tense.
Questions can have the same verb but its meaning changes depending on if the question is in the present simple or present continuous. For example: